Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing components by injecting melted material into a mould, or mold. Injection molding will be performed with a bunch of materials mainly including metals, glasses, elastomers, confections, and most typically thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the half is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. When a product is designed, typically by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are created by a mould-maker from metal, typically either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to create the features of the specified part. Injection molding is widely used for manufacturing a range of elements, from the tiniest elements to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, utilizing photopolymers that don’t soften throughout the injection molding of some lower-temperature thermoplastics, will be used for a few easy injection moulds.
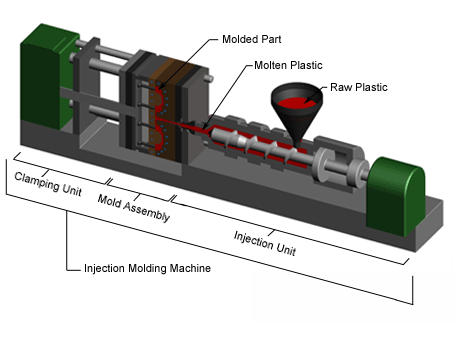
Injection molding uses a special-purpose machine that has 3 parts: the injection unit, the mould and therefore the clamp. parts to be injection-molded should be very carefully designed to facilitate the molding process; the material used for the half, the specified form and options of the half, the material of the mould, and therefore the properties of the molding machine should all be taken into consideration. The versatility of injection molding is facilitated by this breadth of design considerations and possibilities.
Mold
A mold is a hollow metal block into which molten plastic is injected to from a certain fixed shape. Although they are not illustrated in the figure shown below, actually there are many holes drilled in the block for temperature control by means of hot water, oil or heaters.
Molten plastic flows into a mold through a sprue and fills cavities by way of runners and gates. Then, the mold is opened after cooling process and the ejector rod of the injection molding machine pushes the ejector plate of the mold to further eject moldings.
Molding
A molding consists of a sprue to introduce molten resin, a runner to lead it to cavities, and products. Since obtaining only one product by one shot is very inefficient, a mold is usually designed to have multiple cavities connected with a runner so that many products can be made by one shot.
If the length of the runner to each cavity is different in this case, the cavities may not be filled simultaneously, so that dimensions, appearances or properties of the moldings are often different cavity by cavity. Therefore the runner is usually designed so as to have the same length from the sprue to each cavity.
Injection molding is used to create many things such as wire spools, packaging, bottle caps, automotive parts and components, toys, pocket combs, some musical instruments, one-piece chairs and small tables, storage containers, mechanical parts, and most other plastic products available today. Injection molding is the most common modern method of manufacturing plastic parts; it is ideal for producing high volumes of the same object.
Usually, the plastic materials are formed in the shape of pellets or granules and sent from the raw material manufacturers in paper bags. With injection molding, pre-dried granular plastic is fed by a forced ram from a hopper into a heated barrel. As the granules are slowly moved forward by a screw-type plunger, the plastic is forced into a heated chamber, where it is melted. As the plunger advances, the melted plastic is forced through a nozzle that rests against the mould, allowing it to enter the mould cavity through a gate and runner system. The mould remains cold so the plastic solidifies almost as soon as the mould is filled.
Different types of injection molding processes
Although most injection molding processes are covered by the conventional process description above, there are several important molding variations including, but not limited to:
- Die casting
- Metal injection molding
- Thin-wall injection molding
- Injection molding of liquid silicone rubber[23]:17–18
- Reaction injection molding
- Micro injection molding
- Gas-assisted injection molding
- Cube mold technology
Robotic molding
Automation means that the smaller size of parts permits a mobile inspection system to examine multiple parts more quickly. In addition to mounting inspection systems on automatic devices, multiple-axis robots can remove parts from the mould and position them for further processes.
Specific instances include removing of parts from the mould immediately after the parts are created, as well as applying machine vision systems. A robot grips the part after the ejector pins have been extended to free the part from the mould. It then moves them into either a holding location or directly onto an inspection system. The choice depends upon the type of product, as well as the general layout of the manufacturing equipment. Vision systems mounted on robots have greatly enhanced quality control for insert molded parts. A mobile robot can more precisely determine the placement accuracy of the metal component, and inspect faster than a human can.
Finally, you must seek for an injection molding business which will handle huge projects. once you got to scale up production, you don’t wish to have to seem for a brand new supplier just because the company turned out to be incapable of doing larger runs.
We at KERONE have a team of experts to help you with your need for Injection Molding Process in various products range from our wide experience.